ESSENTIAL OPERATING SYSTEM APPLICATIONS
Essential operating system applications:
- Terminal emulator
- Text editor
- Synaptic (GUI package manager)
- Gdebi
- Task manager (System monitor)
1.Terminator - Terminal emulator
Using Linux you will need a terminal.
Terminator is a good terminal emulator with tab support (several tabs in one window) and can be split into some terminal portions from the original, both horizontally and vertically.
sudo apt-get install terminator
Some useful keyboard shortcuts:
- F11: Toggle fullscreen
- Ctrl + Shift+ O: Split terminals horizontally
- Ctrl + Shift+ E: Split terminals vertically
- Ctrl + Shift+ T: Open new tab
2. Geany - Text editor
All configuration files of Linux are text.
I was familiar with Geany because it came as default with Crunchbang, my beloved distro.
sudo apt-get install geany
geany are combined with gksudo to edit system files:
Do not combine it with sudo (it will mess up Geany configuration file and deem it unusable). Using GUI applications with gksu instead of sudo is a rule of thumb.
gksudo geany /etc/fstab #to edit fstab file
Just remember this rule: sudo are for applications in the terminal. For Graphical ones, you need to use gksudo instead.
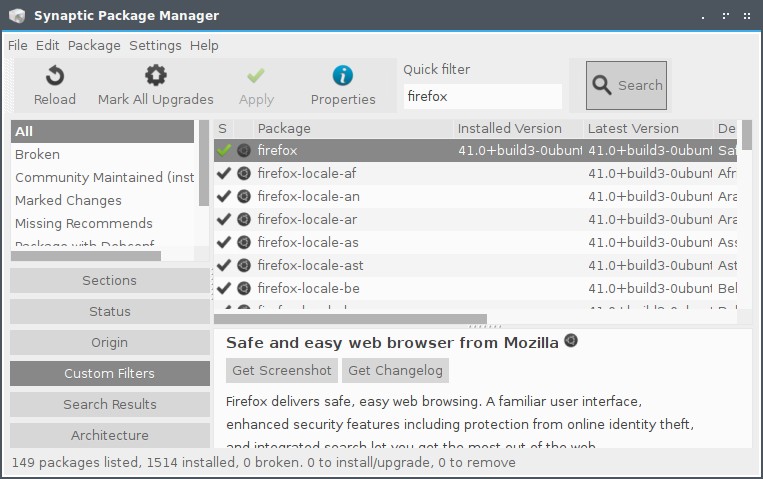
3. Synaptic - GUI package manager
There is another way to install them via a GUI package using Synaptic. It is especially useful when I need to find a recommended package for a specific need.
sudo apt-get install synaptic
Here is how the status of Firefox and its recommends are showing in Synaptic:
4. Gdebi - installer of .deb package
Gdebi is a nice program to handle .deb files - the standard package type in Debian.
After having Gdebi installed, whenever you want to install a .deb file, just choose to open that file with Gdebi.
Installing a .deb package from any other source rather than the official repositories is a frown upon practice. You should REALLY know what you are doing.
sudo apt-get install gdebi
Another alternative to install .deb files: dpkg command. It is available with any Debian/ Ubuntu system.
sudo dpkg -i deb_package #(to remove: sudo dpkg -r deb_package)
5. htop - Task manager (System monitor)
Htop is a lightweight program and does the job just fine.
sudo apt-get install htop
In your terminal emulator, type htop, it will display all the running processes and the resources being used in real time.
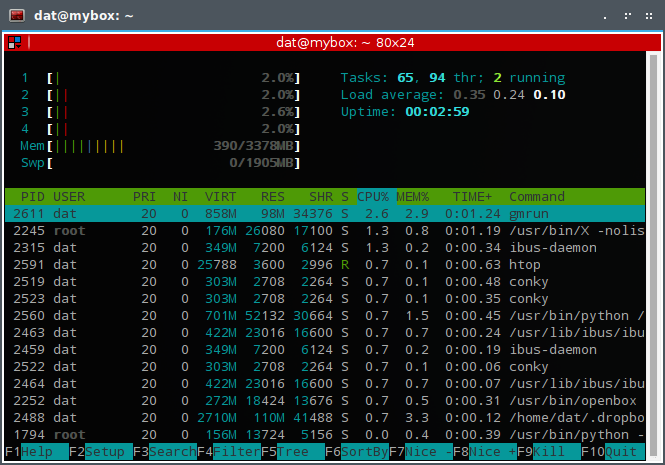
As you can see here, with an Ubuntu 64bit the amount of RAM it took on my system was just 390MB. It is actually great compared with other desktop environments.
Here is how to bind the “familiar” combination keys Ctrl + Alt + Del to htop in my Openbox rc.xml configuration file:
<keybind key="C-A-Delete">
<action name="Execute">
<startupnotify>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<name>htop</name>
</startupnotify>
<command>terminator -e htop</command>
</action>
</keybind>
Leave a comment